Sodalite - Na8Al6Si6O24Cl2
Named from its chemical composition, sodalite was discovered in 1811 in the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex in Greenland. The soldalite group feldspathoids are based on the cubic structure, which is a tektosilicate framework. One half the Si
4+ are replaced by Al
3+ requiring additional cations for charge balance. The open structure affords an equivalent of two very large cavities per unit cell, which accommodate large cations (Cl
-, S
2 or SO
42-) surrounded by Na
+ or Ca
2+ in tetrahedral coordination. The large anions and cations distinguish minerals of the sodalite group:
Sodalite: Na
8Al
6Si
6O
24Cl
2
Hackmanite: Na8Al6Si6O24 (Cl,S)
2
Noselite: Na
8Al
6Si
6O
24Cl
2(SO
4)
Hauyne: (Na,Ca)
4-8Al
6Si
6(O,S)
24(SO
4,Cl)
1-2
Lazurite (Lapis lazuli): (Na,Ca)
8Al
6Si
6O
24(So
4,S,Cl)
2
The sodalite minerals are characteristic of alkaline, undersaturated igneous rocks. Sadalite is most common in Nepheline Syenite and related rock type in association with Nepheline, cancrinite and alkali feldspar.
Optical properties:
•
Form: Commonly form euhedral crystals of dodecahedron habit yielding hexagonal sextion
•
Color: Colorless to pale gray-blue
•
Relief: Moderate negative relief
•
Birefringence: Isotropic
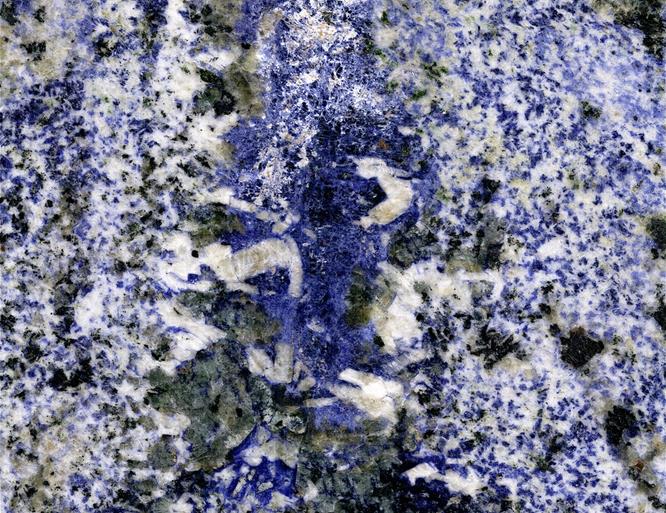
Blue soldalite in a syenite. Itabuna Syenite Complex, Fazenda Hiassu, Bahia State, Brazil. From James St. John
Bibliography
• Cox et al. (1979): The Interpretation of Igneous Rocks, George Allen and Unwin, London.
• Howie, R. A., Zussman, J., & Deer, W. (1992). An introduction to the rock-forming minerals (p. 696). Longman.
• Le Maitre, R. W., Streckeisen, A., Zanettin, B., Le Bas, M. J., Bonin, B., Bateman, P., & Lameyre, J. (2002). Igneous rocks. A classification and glossary of terms, 2. Cambridge University Press.
• Middlemost, E. A. (1986). Magmas and magmatic rocks: an introduction to igneous petrology.
• Shelley, D. (1993). Igneous and metamorphic rocks under the microscope: classification, textures, microstructures and mineral preferred-orientations.
• Vernon, R. H. & Clarke, G. L. (2008): Principles of Metamorphic Petrology. Cambridge University Press.
Photo
.jpg)
Eudialite (high relief and with white-pale pink color) with sodalite (colorless) inclusion in a Naujaite. Ilímaussaq, Greenland. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Eudialite (gray) with sodalite (isotropic) inclusion in a Naujaite. Ilímaussaq, Greenland. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Eudialite (high relief and with white-pale pink color) and aegirine crystals surrounded by sodalite (colorless) in a Naujaite. Ilímaussaq, Greenland. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Eudialite (gray) surrounded by sodalite (isotropic) inclusion in a Naujaite. Ilímaussaq, Greenland. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
K-feldspar with sodalite (isotropic) inclusion. Sodalite is surrounded by cancrinite (high interference colors). Ilímaussaq, Greenland. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
K-feldspar with sodalite (isotropic) inclusion. Sodalite is surrounded by cancrinite (high interference colors). Ilímaussaq, Greenland. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
K-feldspar with sodalite (isotropic) inclusion. Sodalite is surrounded by cancrinite (high interference colors). Ilímaussaq, Greenland. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
K-feldspar with sodalite (isotropic) inclusion. Sodalite is surrounded by cancrinite (high interference colors). Ilímaussaq, Greenland. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
K-feldspar with sodalite (isotropic) inclusion. Sodalite is surrounded by cancrinite (high interference colors). Ilímaussaq, Greenland. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
K-feldspar with sodalite (isotropic) inclusion. Sodalite is surrounded by cancrinite (high interference colors). Ilímaussaq, Greenland. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Eudialite (high relief and with white-pale pink color) with sodalite (colorless) inclusion in a Naujaite. Ilímaussaq, Greenland. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Eudialite (gray) with sodalite (colorless) inclusion in a Naujaite. Ilímaussaq, Greenland. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (marked as Sdl), biotite (green) and colorless alkali feldspar. PPL image , 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (isotropic), biotite and alkali feldspar. XPL image , 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (marked as Sdl), biotite (green) and colorless alkali feldspar. PPL image , 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (isotropic), biotite and alkali feldspar. XPL image , 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (isotropic), titanite and alkali feldspar. XPL image , 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (marked as Sdl), biotite (green) and colorless alkali feldspar. PPL image , 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (isotropic) and alkali feldspar. XPL image , 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (isotropic) and alkali feldspar. XPL image , 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (isotropic), biotite and alkali feldspar. XPL image , 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (marked as Sdl) and colorless alkali feldspar. PPL image , 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (marked as Sdl) and colorless alkali feldspar. PPL image , 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Sodalite (marked as Sdl) and colorless alkali feldspar. PPL image , 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |



.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)